
IR Coatings
Advanced coatings for every application
Optical infrared coatings for demanding applications
Optical systems for infrared wavelengths can be additionally enhanced with optical coatings. A distinction is made between three basic functions:
- Reflection,
- Wavelength filtering and
- Anti-reflection coating.
For more information, see also our blog post “High-performance optical coating”. All coatings also protect the surface of the optics and retain their optical quality even under demanding environmental conditions, such as extreme temperature fluctuations and humidity.
Application areas for IR coatings
Application areas for the use of infrared radiation are manifold. Each sensor benefits from more photons with less interference, so more accurate results are obtained using optical coatings. Spectrometers and LIDAR systems also benefit from such improvements.
The property of all heat sources to emit infrared radiation is used to observe forest fires, the climate or moving objects. In addition, people or fires can be detected through smoke and dust. This supports the work of firefighters and security forces. Infrared based gas analysis is used for medical purposes and in agriculture (for example in biogas plants).
However, it should also be mentioned that the use of highly refractive IR materials in high-performance lenses is unthinkable without AR coatings. Learn more about AR coatings from asphericon.
Specification of the infrared range
Infrared is usually referred to a wavelength of 0.78 μm. Up to 1.4 μm, the range of short-wave NIR (Near Infrared) is located. Between 1 and 3 μm, the radiation is also referred as SWIR (Short Wavelength IR), the exact limits of the spectrum differ depending on the literature. MWIR (Mid Wavelength IR) begins after SWIR and extends to 5.5 μm. Beams with 8 to 14 μm wavelength are assigned to the LWIR (Long IR) range. For IR applications, it is critical that all components of the optics are designed and optimized for the intended wavelengths. For example, fused silica is transparent to infrared radiation up to and including the SWIR spectrum and resistant to chemical and thermal stress.
IR made by asphericon
asphericon offers highly resistant infrared coatings for any application at wavelengths up to 5.1 μm based on the so-called sputtering process. This technology uses ions to extract atoms from a material, which are then deposited in a thin layer on the optics to form the coating. Based on the ion source, a distinction is made between magnetron sputtering and ion beam sputtering methods. In magnetron sputtering, the argon ions are focused to the target via field line trajectories, whereas ion beam sputtering uses its own targeted ion source. By these methods a very stable and uniform layer can be formed, which can withstand even extreme environmental conditions.
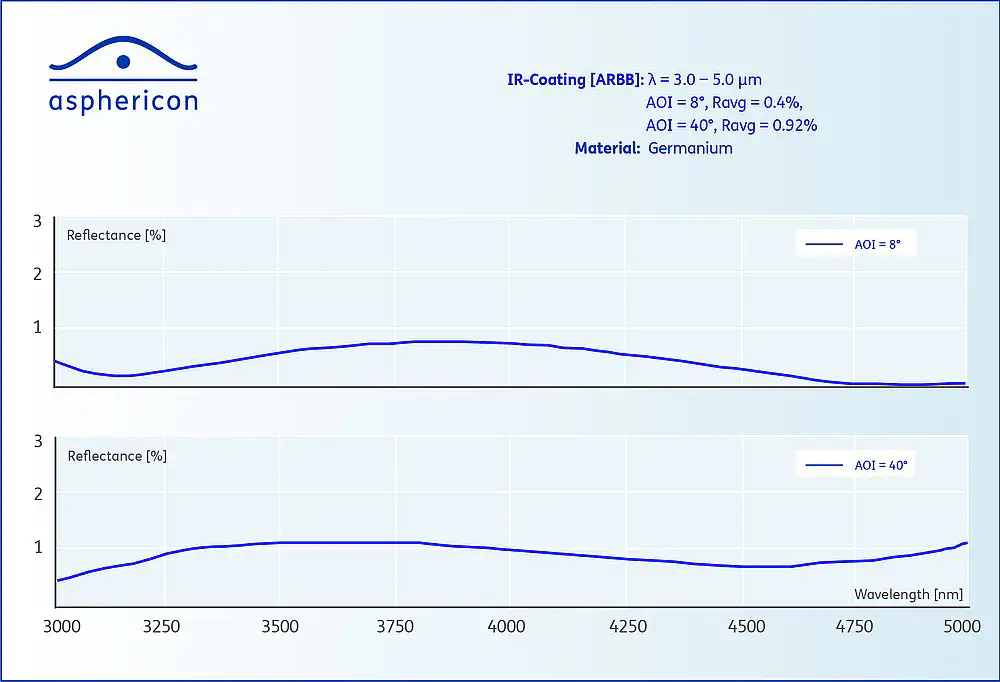 Fig. 2: Example curves for an IR coating on germanium at a reflection of 8° resp. 40 °.
Fig. 2: Example curves for an IR coating on germanium at a reflection of 8° resp. 40 °.In addition, asphericon offers a wide range of environmental tests for all common standards (DIN-, ISO-, MI-L, DO-). Among other things, our IR coatings meet demanding requirements in terms of adhesion, moisture and temperature resistance. Modern manufacturing and measurement technologies transform your specifications into a finished product.
IR coatings from asphericon - Specifications at a glance
- Substrate size: up to 220 mm
- Spectral range: up to 5.1 μm
- Materials: glass, fused silica, crystals, semimetals (e.g. germanium, silicon)
- Stability: ultra-hard coatings (sputtering process)
Curves with specific information about the respective coating can be found on the service page for optical coating and in the download area.
