Laser Scanning
Laser beam shaper and mirrors for non-contact measurement and quality control
Laser scanners use a laser beam to scan surrounding objects and determine their surface and shape. They are used in particular for scanning bar codes and analyzing bodies, the so-called 3D laser scanning.
Barcode scanning
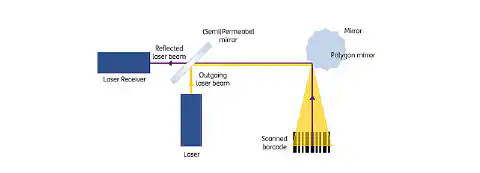
When scanning a barcode, the reflected light is interpreted: A rotating wheel with several mirrors guides a laser beam over the bar code. The different reflections of the black lines and the white gaps are transmitted via the rotating mirror wheel to an optical receiver and evaluated (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Structure of a laser scanner for barcodes
3D Laser Scanning
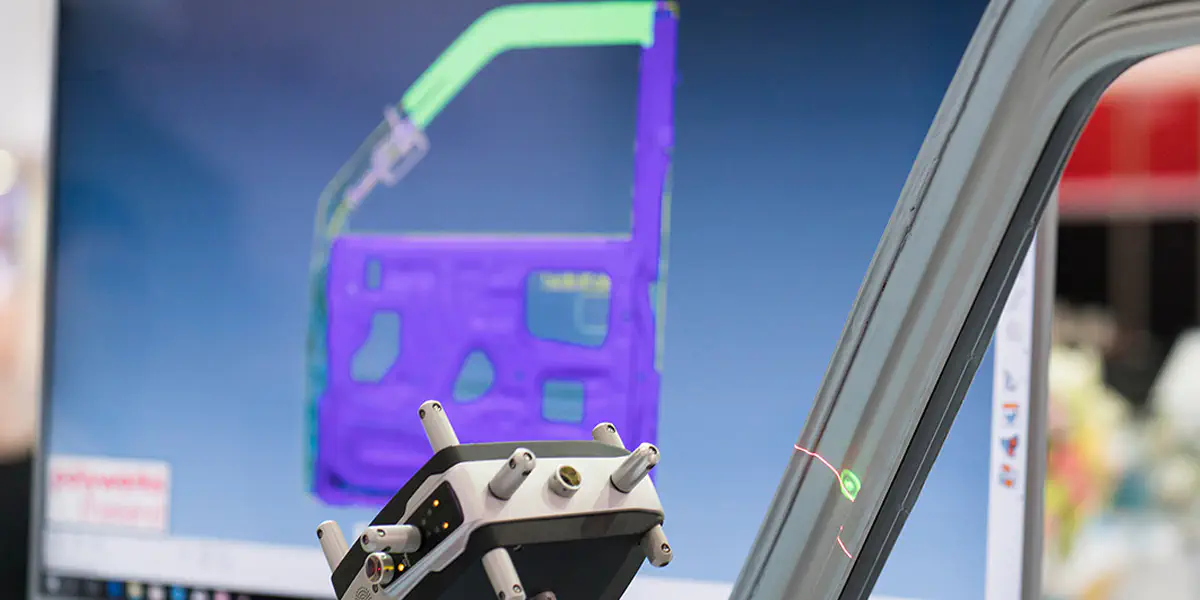
In 3D laser scanning, the time difference between emitted and reflected laser beams is transformed into a 3D model. For this purpose, a laser scans the surrounding objects and spatial conditions via a rotating mirror wheel in a fine grid. When the laser beam is emitted, a timer starts to run and stops measuring its time only when the beams reflected by the objects have been converted into an electrical signal by a photodiode inside a laser light receiver. Through a coupling with software systems and through the determined time, it is possible to transform the scanned bodies and surfaces into a 3D model and visualize them on a display. In addition, a statement about the brightness of the bodies can be made about the reflected light intensity. From the information obtained from the many thousands of individual points, a point cloud is created which is based on three-dimensional coordinates and grey values of the measured surface points. The numerous measuring points allow fast, realistic and reproducible imaging of the scanned objects.
Areas of application of laser scanning
While barcode laser scanning is mainly used in areas such as goods logistics and purchasing, 3D laser scanning offers a wide range of applications. The non-contact measuring method is also suitable for hard-to-reach and complex objects such as bridges or roof constructions. In architecture, laser scanning is used, for example, to calculate and plan facade measurements. In the field of monument preservation, it can be used to determine the current state of historical buildings, which, for example, provide valuable information for the planning of construction measures. The digital recording of factories and their plants is used for the planning of modernization and conversion measures. Another advantage is the continuous production, which saves time and money.
3D laser scans are also used in the area of quality control. Scanned products are compared with stored target models based on their geometry. Deviations from the ACTUAL form to the TARGET form are shown in color and guarantee efficient production and manufacturing. In different phases of production, deformations or corrosion of products, for example, can be detected by comparison measurements.
The film industry uses 3D laser scans for the digital visualization of film locations. For example, lighting and camera paths can be planned. The gaming industry uses laser-scanned locations to model virtual realities.
Laser scanners require various high-quality optics, from beam shaping systems to semi-transparent mirrors. asphericon offers a wide range of high-quality optics and additional coatings that ideally adapt your laser scanner to your requirements.